2011年04月04日
Tubote, Tibet and the Power of Naming

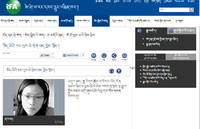
懸鉤子:承蒙史伯嶺教授的允許,我在此將他的〈圖伯特、Tibet 與命名的力量〉之原文全文刊載出來。上圖是傑袞本寺的僧人。
In the course of preparing a Chinese translation of the book Authenticating Tibet, edited by Anne-Marie Blondeau and Katia Buffetrille, the seemingly banal question of the Chinese name for Tibet turned out to be rather problematic. The familiar name “Xizang” 西藏 is historically a very recent term and designates “Tibet” solely in the sense of the territory encompassed within the Tibet Autonomous Region. Thus, in discussing Tibet as an integral historical unit the name is clearly of limited utility and can create confusion. Indeed, it is due to the specific limitations of that term that it was decided that the Chinese edition of Authenticating Tibet would employ the term “Tubote” 圖伯特, a name that is used now by a growing number of writers and bloggers on both sides of the Taiwan Straits. As a result, I prepared the following introductory essay for the Chinese-language edition of Authenticating Tibet in order to explain the choice while at the same time pointing out that the term “Tubote”is not a recent concoction: it has a history as a recognized Chinese-language designation for Tibet. The broader question covered in this introduction is indicated by its very title, which in English is “Tubote, Tibet, and the Power of Naming.”
Authenticating Tibet, which has been quite successful in French and English as a guide to understanding the myriad elements that make up the Tibet Question, will soon be available to those who read Chinese in an edition published this spring by Avant-garde Publishers in Taipei under the title 遮蔽的圖伯特:國際藏學家解讀西藏百題問答. It should be available in bookstores and for purchase online shortly.
My deep thanks to 謝惟敏 for her impeccable translation of this introduction.
TUBOTE, TIBET, AND THE POWER OF NAMING
/ Elliot Sperling
唐曰烏斯國、明曰烏斯藏、
今曰圖伯特、又曰唐古忒
–西藏誌
“In the Tang it was called it Wusiguo, in the Ming, Wusi-Zang.
Today it is called Tubote, and also Tangut.”
—Xizang zhi
The above quote, from an anonymous 18th-century gazetteer (fangzhi 方志) of Tibet[1], may strike readers as a bit of arcane Tibetology, a peculiar remark about nomenclature in the early-Qing era that, while curious, is of little relevance to present-day understanding of the Tibet Issue. And indeed it is curious: the author states that in his day “Tibet” was known as “Tangut” and as … well, “Tibet,” for that is exactly the name that is transcribed in his work as “Tubote 圖伯特.” But is this irrelevant to the modern reader? To the contrary; the author, by telling us that the name “Tubote” was known in the Qing as a name for Tibet, touches upon one of the fundamental questions that confronts anyone writing in Chinese about Tibet at the beginning of the 21st century: what should one call this large land when writing about it as an integral cultural and national whole and not simply as a grouping of administrative divisions within the People’s Republic of China?
The immediacy of this question has been obscured in large part because of the rigidity that the terminology for Tibet and Tibetans has attained in the PRC. But that very rigidity should long ago have led us to question the whole terminological edifice. Ideological and post-modern jargon (and gibberish) aside, language, in this instance, is indeed power. China’s ability to command the terminology associated with Tibet has consequently given it the ability to define Tibet and to define Tibetans. It has allowed China the power to determine the most basic terms of debate over Tibet, a debate that readers of this volume will shortly encounter in the chapters that follow.
It is therefore fascinating to see that a growing number of writings and blog posts in the Chinese language—many from Taiwan, some by Tibetan writers, and even a few from the PRC that manage to make it past the Great Firewall of China—pick up where our anonymous 18th-century author has left off and refer to Tibet as just that: Tubote or, as a variant, Tubo 圖伯. It is for reasons that are spelled out in this introductory note that Tubote is used in this book for the world of Tibetan civilization and of the Tibetan people, a world that stretches far beyond today’s Tibet Autonomous Region. [2]
The official term, the term for Tibet that most people use in Chinese, is Xizang 西藏. Its etymology is well known and transparently obvious from references in the standard dynastic histories and other commonly-used sources. One notion common among Western Tibet supporters, that Xizang means “Treasure House of the West” and is so named because China sees the area as a massive storehouse of mineral wealth to be exploited, is patently erroneous. The “Zang” in Xizang, while it can mean a storehouse, is used in the name simply because it transcribes Gtsang, one part of the region generally referred to as Central Tibet, or Dbus-Gtsang in Tibetan. In the Ming period we find Dbus-Gtsang rendered as Wusi-Zang 烏斯藏.[3] During the Qing this changes to Wei-Zang (again, an easily understood transcription of Dbus-Gtsang)[4] and finally to Xizang. The last denotes the Western location (i.e., “Xi” 西) of the land and the sound of its two syllables finds an echo in the name of the province Republican China created for Khams, the southeastern part of Tibet: Xikang 西康 (a good portion of which actually lay beyond China’s reach).
As a result of all this, however, “Xizang” remains identified only with Central Tibet and a part of Khams. And it is that sense, and that sense alone, that is conveyed by the term. But the greater world of Tibetan Studies, and indeed of Tibetan perceptions, sees Tibet as the land of Tibet’s three principle regions: Central Tibet (Dbus-Gtsang), Khams and A-mdo. And many writers and bloggers from Taiwan, China, and Tibet, increasingly understand this. Thus the growth in the use of Tubote (or Tubo) to denote what Tibetans understand as Tibet. There is obviously something a bit subversive in this: Tibetans using a name of their own choosing in Chinese-language materials are retaking some of what has been lost to them and acting to define themselves.
The entire vocabulary of nationalities and nationality terms in the PRC is imbued with a conscious political element of control by definition. The very designation “minority nationality” reduces all of the peoples so designated to the same uniform level, regardless of whether they number in the millions and have a conscious history of themselves as a political power with their own government and a bureaucracy literate in their own language, or whether they number in the tens of thousands with no national history.
It would be wise to remember too that the meaning of Xizang is essentially determined by politics: during the era of Guomindang rule the territory was considerably smaller than it is presently, since a good portion of Khams (and even a bit of Dbus) was drawn into the map of Guomindang Xikang. It goes without saying that Qinghai and the Tibetan areas of present-day Yunnan and Gansu were not covered by the pre-1949 definition of Xizang, just as they are not covered by it today. And so the traditional and historic realm of Tibet does not have a single officially-sanctioned Chinese term designating it today. It can be described, of course, in phrases like Zangzu juzhu diqu 藏族居住地区 , “the area inhabited by the Tibetan nationality.” But that is a description, not a name. Obviously there are solid fundamental reasons to find writers gravitating to the term “Tubote.”
The language about the area of Tibet has also encumbered the language about Tibetans with a singular inelegance. If only Xizang can be understood to denote Tibet, and Xizang/Tibet is to be limited to the TAR, an artificial stiffness attaches to descriptions of Tibetans as a whole. They can be described as people “of Tibetan nationality,” Zangzu 藏族, but “Tibetans,” Xizang ren 西藏人, are uniquely the residents of the TAR. In Tibetan this divide is manifested in the distinction between the terms Bod-pa (=Tibetan, Xizang ren) and Bod-rigs (=those of Tibetan nationality, Zangzu). That this is a recently created distinction is clear from some of the common accounts of the Red Army’s passage through regions in Khams during the Long March. In these writings one finds a Chinese awareness that prior to 1949 at least, the use of the Tibetan term Bod-pa (i.e., “Xizang ren”) was not restricted to the area under the jurisdiction of the Dalai Lama’s government (i.e. the modern TAR). Thus one can read of the Red Army’s establishment of short-lived, local “Tibetan People’s Governments” which they called “Boba renmin zhengfu” 波巴人民政府, Boba 波巴 transcribing the Tibetan Bod-pa. [5]
Tibetan aside, all modern languages except Chinese refer to the entire cultural and historic realm of the Tibetans with a variant of the name Tibet. And in those other languages the rigid distinctions engendered in modern Chinese that are deployed in support of China’s political definition of Tibet and Tibetans don’t apply. The increasing numbers of writers and bloggers from Taiwan and also from the PRC opting for Tubote shows that their engagement with the question is substantive. In addition to Tubote, many of them have chosen to integrate into their writing transcriptions of Tibetan terms for Tibetans as a people (Bomi 博彌 and Boba 博巴, i.e., Bod-mi and Bod-pa in Tibetan), Tibetan as a language (Boyi 博伊 and Bogai 博蓋 , i.e., Bod-yig and Bod-skad), and so forth, all in order to avoid the limits imposed by the use of the Chinese term Zang 藏, with its connection to “Xizang.”
Ironically, the one place in the Chinese language where “Bod” is decreed to be appropriate in Chinese transcriptions referring to Tibet is actually in the mandated pronunciation of the name for Tibet used during the Tang period: Tufan 吐蕃, now pronounced and rendered everywhere in the PRC in romanized pinyin as Tubo. This pronunciation was rigorously dissected and clearly shown to be erroneous a century ago by Paul Pelliot 伯希和. Indeed, I recall with some humor a conference many years ago at which a Chinese colleague kept referring to “the Tubo Kingdom.” A venerable Tibetologist leaned over to me and whispered “Will nobody have pity on the poor man and tell him that Pelliot showed already in 1915 that the character can’t be read bo?” Of course our Chinese colleague was likely familiar with Pelliot’s comments; but politics is no doubt at play here and the notion that the name Bod was known to the Tang and incorporated into the contemporary Chinese name for the Tibetan state is an element in the Marxist teleology that cannot be trifled with: it ostensibly demonstrates that even at that early stage the Tibetan and Chinese peoples were inexorably growing closer and closer.
Interestingly, as Pelliot showed, the desire to see Tufan as Tubo, and to see the name Bod within the Chinese transcription is not rooted in Chinese historiographical traditions but derives from the 19th century work of Western Orientalists, stretching from Jean-Pierre Abel Rémusat to William Woodville Rockhill and beyond. We might note that even if one were to accept that fan 蕃 should be read as bo, that still leaves us with the problem of explaining the first character, Tu 吐, and here imaginations have run riot, with some of the Orientalists mentioned by Pelliot fantasizing about “Mtho-Bod” or “Stod-Bod” as names used in ancient Tibet. Both names render something akin to “High Tibet” or “Upper Tibet.” These names, however, are unattested in old Tibetan materials. Most importantly they do not appear in bilingual materials from Tibet’s imperial period in which Tufan is simply rendered as Bod. Without such attestations “Stod-Bod” and “Mtho-Bod” appear like nothing more than the result of a 19th-century hunt through dictionaries and word lists aimed at concocting a name that didn’t exist.
Actually, the Tibetan Plateau didn’t constitute one realm to its pre-Tang inhabitants. Everything we know about the Tibetan Plateau before and during the early period of the empire speaks of a divided realm with no visible cohesion—ethnically, linguistically, and religiously—and no evidence whatsoever of a larger sense of “Bod” until the Tibetan emperors and their armies rolled through the lands of the ’A-zha 吐谷渾, the Sum-pa 松巴, Zhang-zhung 祥雄, the Khyung-po 瓊波, and others, and created it. Nevertheless, we do have evidence of the early use of the name Bod, but this only comes from the south-central area of the Plateau and our awareness of this is due to the Indian references to “Bhoṭa” in Vedic literature: it was not a name used across the Plateau before imperial times. How, indeed, could it have been otherwise, given the disunity among the plateau’s inhabitants in pre- and early imperial times? The idea that all people living on the Tibetan Plateau during that period saw themselves as holders of a common name, or that they were all aware of the topography of the world beyond the Plateau and thus commonly considered their realm to be “Upper” or “High Tibet” is utterly unsustainable.
The fact is, as Pelliot showed in 1915, there is a fine and reasonable explanation for the name Tufan in the official Tang histories. Indeed, we find at the beginning of the Jiu Tangshu 舊唐書, a description of its derivation from the Xianbei 鮮卑 clan name Tufa 禿髮, carried by the descendants of a Southern Liang 涼 family: 以禿髮為國號,語訛謂之吐蕃. In other words, Tufan became the name for Tibet as the result of an error in rendering Tufa, the correct Chinese name. And it was this clan name Tufa that was originally applied to Tibet; only later was it corrupted into Tufan. Tufa, in fact, actually would have been pronounced in a manner akin to “Tupat,” which can be easily linked to the forms for “Tibet” subsequently found in Turkic, Arabic, and a number of other languages, and which eventually surfaced in European languages. Indeed, we find the term adopted by the 8th-century Turks as Tüpüt; from there it passed on to the Arabs and the Persians in the form of Tubbat and similar variants. In the later Middle Ages the name is recorded by Marco Polo as Tebet; the narrative accounts of other medieval European travelers use related spellings.
The long journey of this clan name and its transformation into a geographical name may seem convoluted, but it is hardly unusual. This is, after all, the case with “America.” Moreover, the transformation of the name for a small region (i.e., Tufa/Tufan, which appears at first only on the northeast edge of the Tibetan Plateau) into the name for a much larger area is also not rare, as the examples of “Asia” and “Africa” illustrate. The field of meaning for both terms expanded well beyond their original senses in the languages of the Classical Mediterranean world. Thus, this somewhat localized pre-Tang name, Tufa/Tufan came to denote in Chinese the larger Tibetan realm that emerged to the west of its original location. This name was quite unrelated to the names that the actual inhabitants used on the plateau itself, much as the name “America” is similarly unrelated to any indigenous names used in the Western Hemisphere.
It is interesting to note that when the scholars Don-grub rgyal 端智嘉 and Chen Qingying 陈庆英 made their Tibetan translation of the Jiu Tangshu and Xin Tangshu 新唐書 chapters on Tibet, they assuredly knew of the old Stod-Bod idea, but they appear to have rejected it, rendering Tufan instead as Thu-Bhod. One imagines that they couldn’t wholly reject the politicized Tubo, which is essentially dogma in the PRC, but they could finesse it, perhaps, by rendering it as something closer to “Tibet” and not outrightly equating fan/bo with Bod.
In brief, then, the original Chinese name for Tibet noted at the beginning of the Jiu Tangshu can now be seen as an early form of the name that is used universally outside Tibet and modern China: Tibet. And Tibet, as universally understood as a cultural and historical realm, is not the modern “Xizang.” But it is the Tubote that a new generation that writes and blogs in Chinese has rediscovered and adopted as a clear and unambiguous marker of the land with which they are so intensely engaged.
[1] Xizang zhi 西藏誌 (Taipei, 1968); See also Deng Ruiling 邓锐龄, “Du ‘Xizang zhi’ zaji,” 读 《西藏志》札记, Zhongguo Zangxue 中国藏学, 2005.2, pp. 18-25.
[2]While there is a modern precedent for using the variant “Tubo,” the fact that Tubote is already found in the Qing (often with the variant forms土伯忒 or 土白特, etc.) and that it more clearly reflects the name by which Tibet is known in almost all the world’s languages recommends it as the form to be used throughout this book. In addition, the present-day Tubo圖伯 is vulnerable to being confused with the erroneous Pinyin rendering of Tufan吐蕃 as “Tubo,” a problem discussed below.
[3]Zhang Tingyu 張廷玉, Mingshi 明史 (Bejing, 1974), 331:8571-8585.
[4]See Songyun 松荺, Wei-Zang tongzhi 衛藏通志 (Taipei, 1965).
[5]Hongjun changzheng zai Sichuan 红军长征在四川, (Chengdu, 1986), p. 355 ff.
[6]Paul Pelliot, “Quelques transcriptions chinoises de noms tibétains,” T’oung Pao 通報 16.1 (March, 1915), pp. 18-20.
[7] Don-grub rgyal and Khrin Chin-dbyin, Thang-yig gsar-rnying-las byung-ba’i Bod chen-po’i srid-lugs = Duanzhi jia端智嘉 and Chen Qingying Qingying 陈庆英, Tufan zhuan吐蕃傳 (Xining, 1983).
/ Elliot Sperling
唐曰烏斯國、明曰烏斯藏、
今曰圖伯特、又曰唐古忒
–西藏誌
“In the Tang it was called it Wusiguo, in the Ming, Wusi-Zang.
Today it is called Tubote, and also Tangut.”
—Xizang zhi
The above quote, from an anonymous 18th-century gazetteer (fangzhi 方志) of Tibet[1], may strike readers as a bit of arcane Tibetology, a peculiar remark about nomenclature in the early-Qing era that, while curious, is of little relevance to present-day understanding of the Tibet Issue. And indeed it is curious: the author states that in his day “Tibet” was known as “Tangut” and as … well, “Tibet,” for that is exactly the name that is transcribed in his work as “Tubote 圖伯特.” But is this irrelevant to the modern reader? To the contrary; the author, by telling us that the name “Tubote” was known in the Qing as a name for Tibet, touches upon one of the fundamental questions that confronts anyone writing in Chinese about Tibet at the beginning of the 21st century: what should one call this large land when writing about it as an integral cultural and national whole and not simply as a grouping of administrative divisions within the People’s Republic of China?
The immediacy of this question has been obscured in large part because of the rigidity that the terminology for Tibet and Tibetans has attained in the PRC. But that very rigidity should long ago have led us to question the whole terminological edifice. Ideological and post-modern jargon (and gibberish) aside, language, in this instance, is indeed power. China’s ability to command the terminology associated with Tibet has consequently given it the ability to define Tibet and to define Tibetans. It has allowed China the power to determine the most basic terms of debate over Tibet, a debate that readers of this volume will shortly encounter in the chapters that follow.
It is therefore fascinating to see that a growing number of writings and blog posts in the Chinese language—many from Taiwan, some by Tibetan writers, and even a few from the PRC that manage to make it past the Great Firewall of China—pick up where our anonymous 18th-century author has left off and refer to Tibet as just that: Tubote or, as a variant, Tubo 圖伯. It is for reasons that are spelled out in this introductory note that Tubote is used in this book for the world of Tibetan civilization and of the Tibetan people, a world that stretches far beyond today’s Tibet Autonomous Region. [2]
The official term, the term for Tibet that most people use in Chinese, is Xizang 西藏. Its etymology is well known and transparently obvious from references in the standard dynastic histories and other commonly-used sources. One notion common among Western Tibet supporters, that Xizang means “Treasure House of the West” and is so named because China sees the area as a massive storehouse of mineral wealth to be exploited, is patently erroneous. The “Zang” in Xizang, while it can mean a storehouse, is used in the name simply because it transcribes Gtsang, one part of the region generally referred to as Central Tibet, or Dbus-Gtsang in Tibetan. In the Ming period we find Dbus-Gtsang rendered as Wusi-Zang 烏斯藏.[3] During the Qing this changes to Wei-Zang (again, an easily understood transcription of Dbus-Gtsang)[4] and finally to Xizang. The last denotes the Western location (i.e., “Xi” 西) of the land and the sound of its two syllables finds an echo in the name of the province Republican China created for Khams, the southeastern part of Tibet: Xikang 西康 (a good portion of which actually lay beyond China’s reach).
As a result of all this, however, “Xizang” remains identified only with Central Tibet and a part of Khams. And it is that sense, and that sense alone, that is conveyed by the term. But the greater world of Tibetan Studies, and indeed of Tibetan perceptions, sees Tibet as the land of Tibet’s three principle regions: Central Tibet (Dbus-Gtsang), Khams and A-mdo. And many writers and bloggers from Taiwan, China, and Tibet, increasingly understand this. Thus the growth in the use of Tubote (or Tubo) to denote what Tibetans understand as Tibet. There is obviously something a bit subversive in this: Tibetans using a name of their own choosing in Chinese-language materials are retaking some of what has been lost to them and acting to define themselves.
The entire vocabulary of nationalities and nationality terms in the PRC is imbued with a conscious political element of control by definition. The very designation “minority nationality” reduces all of the peoples so designated to the same uniform level, regardless of whether they number in the millions and have a conscious history of themselves as a political power with their own government and a bureaucracy literate in their own language, or whether they number in the tens of thousands with no national history.
It would be wise to remember too that the meaning of Xizang is essentially determined by politics: during the era of Guomindang rule the territory was considerably smaller than it is presently, since a good portion of Khams (and even a bit of Dbus) was drawn into the map of Guomindang Xikang. It goes without saying that Qinghai and the Tibetan areas of present-day Yunnan and Gansu were not covered by the pre-1949 definition of Xizang, just as they are not covered by it today. And so the traditional and historic realm of Tibet does not have a single officially-sanctioned Chinese term designating it today. It can be described, of course, in phrases like Zangzu juzhu diqu 藏族居住地区 , “the area inhabited by the Tibetan nationality.” But that is a description, not a name. Obviously there are solid fundamental reasons to find writers gravitating to the term “Tubote.”
The language about the area of Tibet has also encumbered the language about Tibetans with a singular inelegance. If only Xizang can be understood to denote Tibet, and Xizang/Tibet is to be limited to the TAR, an artificial stiffness attaches to descriptions of Tibetans as a whole. They can be described as people “of Tibetan nationality,” Zangzu 藏族, but “Tibetans,” Xizang ren 西藏人, are uniquely the residents of the TAR. In Tibetan this divide is manifested in the distinction between the terms Bod-pa (=Tibetan, Xizang ren) and Bod-rigs (=those of Tibetan nationality, Zangzu). That this is a recently created distinction is clear from some of the common accounts of the Red Army’s passage through regions in Khams during the Long March. In these writings one finds a Chinese awareness that prior to 1949 at least, the use of the Tibetan term Bod-pa (i.e., “Xizang ren”) was not restricted to the area under the jurisdiction of the Dalai Lama’s government (i.e. the modern TAR). Thus one can read of the Red Army’s establishment of short-lived, local “Tibetan People’s Governments” which they called “Boba renmin zhengfu” 波巴人民政府, Boba 波巴 transcribing the Tibetan Bod-pa. [5]
Tibetan aside, all modern languages except Chinese refer to the entire cultural and historic realm of the Tibetans with a variant of the name Tibet. And in those other languages the rigid distinctions engendered in modern Chinese that are deployed in support of China’s political definition of Tibet and Tibetans don’t apply. The increasing numbers of writers and bloggers from Taiwan and also from the PRC opting for Tubote shows that their engagement with the question is substantive. In addition to Tubote, many of them have chosen to integrate into their writing transcriptions of Tibetan terms for Tibetans as a people (Bomi 博彌 and Boba 博巴, i.e., Bod-mi and Bod-pa in Tibetan), Tibetan as a language (Boyi 博伊 and Bogai 博蓋 , i.e., Bod-yig and Bod-skad), and so forth, all in order to avoid the limits imposed by the use of the Chinese term Zang 藏, with its connection to “Xizang.”
Ironically, the one place in the Chinese language where “Bod” is decreed to be appropriate in Chinese transcriptions referring to Tibet is actually in the mandated pronunciation of the name for Tibet used during the Tang period: Tufan 吐蕃, now pronounced and rendered everywhere in the PRC in romanized pinyin as Tubo. This pronunciation was rigorously dissected and clearly shown to be erroneous a century ago by Paul Pelliot 伯希和. Indeed, I recall with some humor a conference many years ago at which a Chinese colleague kept referring to “the Tubo Kingdom.” A venerable Tibetologist leaned over to me and whispered “Will nobody have pity on the poor man and tell him that Pelliot showed already in 1915 that the character can’t be read bo?” Of course our Chinese colleague was likely familiar with Pelliot’s comments; but politics is no doubt at play here and the notion that the name Bod was known to the Tang and incorporated into the contemporary Chinese name for the Tibetan state is an element in the Marxist teleology that cannot be trifled with: it ostensibly demonstrates that even at that early stage the Tibetan and Chinese peoples were inexorably growing closer and closer.
Interestingly, as Pelliot showed, the desire to see Tufan as Tubo, and to see the name Bod within the Chinese transcription is not rooted in Chinese historiographical traditions but derives from the 19th century work of Western Orientalists, stretching from Jean-Pierre Abel Rémusat to William Woodville Rockhill and beyond. We might note that even if one were to accept that fan 蕃 should be read as bo, that still leaves us with the problem of explaining the first character, Tu 吐, and here imaginations have run riot, with some of the Orientalists mentioned by Pelliot fantasizing about “Mtho-Bod” or “Stod-Bod” as names used in ancient Tibet. Both names render something akin to “High Tibet” or “Upper Tibet.” These names, however, are unattested in old Tibetan materials. Most importantly they do not appear in bilingual materials from Tibet’s imperial period in which Tufan is simply rendered as Bod. Without such attestations “Stod-Bod” and “Mtho-Bod” appear like nothing more than the result of a 19th-century hunt through dictionaries and word lists aimed at concocting a name that didn’t exist.
Actually, the Tibetan Plateau didn’t constitute one realm to its pre-Tang inhabitants. Everything we know about the Tibetan Plateau before and during the early period of the empire speaks of a divided realm with no visible cohesion—ethnically, linguistically, and religiously—and no evidence whatsoever of a larger sense of “Bod” until the Tibetan emperors and their armies rolled through the lands of the ’A-zha 吐谷渾, the Sum-pa 松巴, Zhang-zhung 祥雄, the Khyung-po 瓊波, and others, and created it. Nevertheless, we do have evidence of the early use of the name Bod, but this only comes from the south-central area of the Plateau and our awareness of this is due to the Indian references to “Bhoṭa” in Vedic literature: it was not a name used across the Plateau before imperial times. How, indeed, could it have been otherwise, given the disunity among the plateau’s inhabitants in pre- and early imperial times? The idea that all people living on the Tibetan Plateau during that period saw themselves as holders of a common name, or that they were all aware of the topography of the world beyond the Plateau and thus commonly considered their realm to be “Upper” or “High Tibet” is utterly unsustainable.
The fact is, as Pelliot showed in 1915, there is a fine and reasonable explanation for the name Tufan in the official Tang histories. Indeed, we find at the beginning of the Jiu Tangshu 舊唐書, a description of its derivation from the Xianbei 鮮卑 clan name Tufa 禿髮, carried by the descendants of a Southern Liang 涼 family: 以禿髮為國號,語訛謂之吐蕃. In other words, Tufan became the name for Tibet as the result of an error in rendering Tufa, the correct Chinese name. And it was this clan name Tufa that was originally applied to Tibet; only later was it corrupted into Tufan. Tufa, in fact, actually would have been pronounced in a manner akin to “Tupat,” which can be easily linked to the forms for “Tibet” subsequently found in Turkic, Arabic, and a number of other languages, and which eventually surfaced in European languages. Indeed, we find the term adopted by the 8th-century Turks as Tüpüt; from there it passed on to the Arabs and the Persians in the form of Tubbat and similar variants. In the later Middle Ages the name is recorded by Marco Polo as Tebet; the narrative accounts of other medieval European travelers use related spellings.
The long journey of this clan name and its transformation into a geographical name may seem convoluted, but it is hardly unusual. This is, after all, the case with “America.” Moreover, the transformation of the name for a small region (i.e., Tufa/Tufan, which appears at first only on the northeast edge of the Tibetan Plateau) into the name for a much larger area is also not rare, as the examples of “Asia” and “Africa” illustrate. The field of meaning for both terms expanded well beyond their original senses in the languages of the Classical Mediterranean world. Thus, this somewhat localized pre-Tang name, Tufa/Tufan came to denote in Chinese the larger Tibetan realm that emerged to the west of its original location. This name was quite unrelated to the names that the actual inhabitants used on the plateau itself, much as the name “America” is similarly unrelated to any indigenous names used in the Western Hemisphere.
It is interesting to note that when the scholars Don-grub rgyal 端智嘉 and Chen Qingying 陈庆英 made their Tibetan translation of the Jiu Tangshu and Xin Tangshu 新唐書 chapters on Tibet, they assuredly knew of the old Stod-Bod idea, but they appear to have rejected it, rendering Tufan instead as Thu-Bhod. One imagines that they couldn’t wholly reject the politicized Tubo, which is essentially dogma in the PRC, but they could finesse it, perhaps, by rendering it as something closer to “Tibet” and not outrightly equating fan/bo with Bod.
In brief, then, the original Chinese name for Tibet noted at the beginning of the Jiu Tangshu can now be seen as an early form of the name that is used universally outside Tibet and modern China: Tibet. And Tibet, as universally understood as a cultural and historical realm, is not the modern “Xizang.” But it is the Tubote that a new generation that writes and blogs in Chinese has rediscovered and adopted as a clear and unambiguous marker of the land with which they are so intensely engaged.
[1] Xizang zhi 西藏誌 (Taipei, 1968); See also Deng Ruiling 邓锐龄, “Du ‘Xizang zhi’ zaji,” 读 《西藏志》札记, Zhongguo Zangxue 中国藏学, 2005.2, pp. 18-25.
[2]While there is a modern precedent for using the variant “Tubo,” the fact that Tubote is already found in the Qing (often with the variant forms土伯忒 or 土白特, etc.) and that it more clearly reflects the name by which Tibet is known in almost all the world’s languages recommends it as the form to be used throughout this book. In addition, the present-day Tubo圖伯 is vulnerable to being confused with the erroneous Pinyin rendering of Tufan吐蕃 as “Tubo,” a problem discussed below.
[3]Zhang Tingyu 張廷玉, Mingshi 明史 (Bejing, 1974), 331:8571-8585.
[4]See Songyun 松荺, Wei-Zang tongzhi 衛藏通志 (Taipei, 1965).
[5]Hongjun changzheng zai Sichuan 红军长征在四川, (Chengdu, 1986), p. 355 ff.
[6]Paul Pelliot, “Quelques transcriptions chinoises de noms tibétains,” T’oung Pao 通報 16.1 (March, 1915), pp. 18-20.
[7] Don-grub rgyal and Khrin Chin-dbyin, Thang-yig gsar-rnying-las byung-ba’i Bod chen-po’i srid-lugs = Duanzhi jia端智嘉 and Chen Qingying Qingying 陈庆英, Tufan zhuan吐蕃傳 (Xining, 1983).
Posted by rosaceae at 00:11│Comments(0)
│史伯嶺教授
※このブログではブログの持ち主が承認した後、コメントが反映される設定です。